AI-Generated Art Detection Project - In this project we learned to explore the application of deep learning techniques for image classification by making an image classifier that recognizes if a given Art Image was generated by an AI or not.
This was done in the context of the course Context Aware Security Analytics In Computer Vision 2023/2024 - UNISA, during my master Degree.
Authors: Katia Melanie Perchet, Franco Nicolas Merenda.
The project is organized by following the next approach:
- Apply CNNs to each Art Style - Classify if image of given Art Style is AI Generated or not.
- Apply CNNs to all Art Styles - Classify if image from any Art Style is AI Generated or not.
During this project, special thanks to Katia 😍, since she was the main lead on this project, where she was in charge of the majority of the project, fine-tuning the models and define the custom model described below. I learned a ton from her during this, about deep learning models, customizations and how to customize parameters. Thank you so much Katita 💕💕.
1.1. Dataset: AI-ArtBench
AI-ArtBench is a dataset that contains 180,000+ art images. 60,000 of them are human-drawn art that was directly taken from ArtBench-10 dataset and the rest is generated equally using Latent Diffusion and Standard Diffusion models. The human-drawn art is in 256x256 resolution and images generated using Latent Diffusion and Standard Diffusion has 256x256 and 768x768 resolutions respectively.
Dataset Information:
- Folders Organization:
AI_<source_model>_<art_style>source_model: Latent Diffusion (LD), Standard Diffusion (SD)art_style:Art Nouveau,Baroque,Expressionism,Impressionism,Post impressionism,Realism,Renaissance,Romanticism,Surrealism,Ukiyo-e
- Total Images Count from All Art Styles:
TrainSplit : 155,015TestSplit : 30,000
1.2. CNN - Models
In this project we have tested different types of CNNs architectures in order to perform good accuracy.
For each Art Style, we tested the following CNNs:
CNN- Defined by Katia
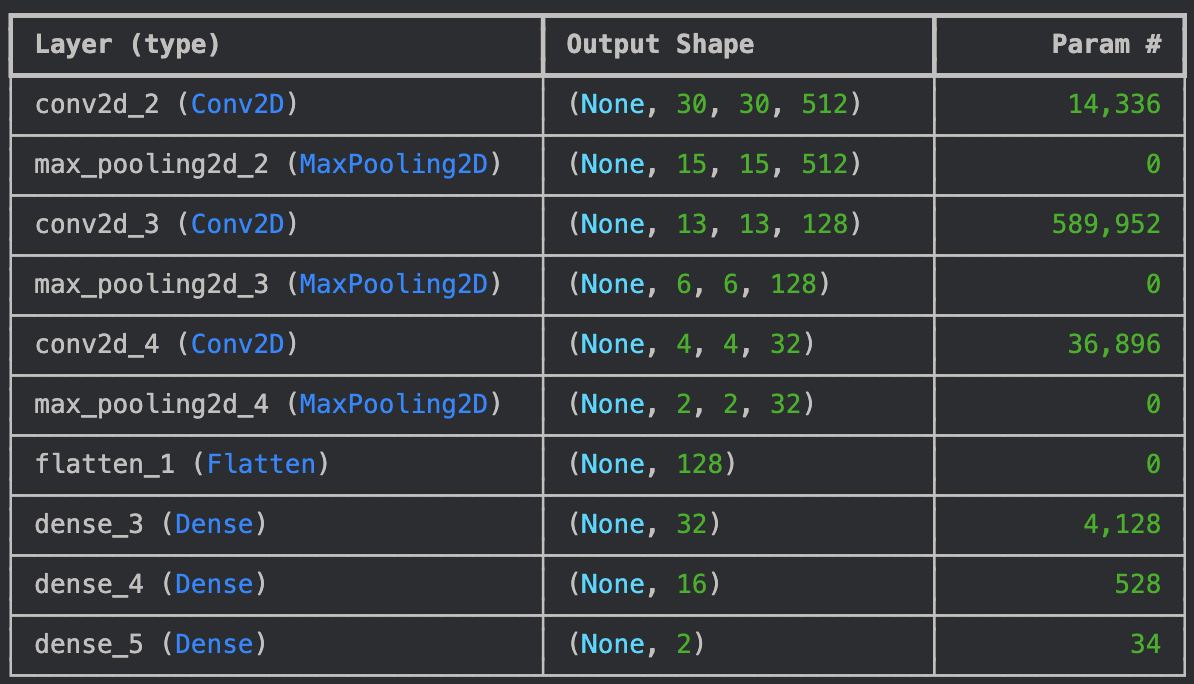
VGG16-(Transfer Learning) + Flatten() + Dense(256, "relu") + Dropout(0.5) + Dense(1, "sigmoid")VGG19-(Transfer Learning) + Flatten() + Dense(256, "relu") + Dropout(0.5) + Dense(1, "sigmoid")
For All Art Styles, we tested the following CNNs:
ResNet50-(Transfer Learning) + Flatten() + Dense(256, "relu") + Dropout(0.5) + Dense(1, "sigmoid")InceptionV3-(Transfer Learning) + Flatten() + Dense(256, "relu") + Dropout(0.5) + Dense(1, "sigmoid")
2. Lessons Learned
While doing this project, we made use of different libraries to build the models, train them and get
Repositories and Links
The full source code and documentation are available on:
- Repository: AI Art Casa - Source Code
- Report PDF: Results - Report PDF
2. Extras
While setting up the environment to train the models on my local machine, I had some issues to take advantage of the Mac M1 GPU. After doing some research, I reached to this point where you can make use of it.
2.1 Using miniforge - conda – MacOS M1/M2 🍎 GPU Support!
Useful Links:
- TensorFlow Installation on Mac M1/M2(Apple Silicon) Chip | Quick Setup Guide
- TensorFlow Setup on Apple Silicon Mac (M1, M1 Pro, M1 Max)
NOTE: Run your terminal in ARM64 Mode. You can use the following aliases to run as ARM or X86.
alias arm="env /usr/bin/arch -arm64 /bin/zsh --login"
alias intel="env /usr/bin/arch -x86_64 /bin/zsh --login"
git clone https://github.com/katiaperchet/ai-art-casa
wget https://github.com/conda-forge/miniforge/releases/latest/download/Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
chmod +x ~/Downloads/Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
sh ~/Downloads/Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
source ~/miniforge3/bin/activate
(Option 1) - Create conda environment with
python=3.11withtensorflow=2.16.2dependencies:i. Create it Step by step
conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps conda create -n tensorflow python=3.11 # Activate created virtual environment conda activate tensorflowii. Install necessary dependencies (Two options):
pip install tensorflow-macos pip install tensorflow-metal conda install numpy=1.26.4 pandas matplotlib scikit-learn scipy plotly jupyter seaborn(Option 2) - Create conda environment from file
conda env create -f conda_macm1_environment.yaml
- Run
jupyter notebookwith GPU support!